The Complex Path to State Recognition: A Deep Dive
Recognizing a new nation isn’t simply a matter of declaring its existence. It’s a nuanced, often protracted process steeped in international law and diplomatic maneuvering. You might wonder what it really takes for a territory to gain a seat at the table of nations. Let’s explore the intricacies of statehood and the delicate dance of international recognition.
What Constitutes a State?
International law doesn’t offer a rigid definition of a “state.” Though, certain criteria are generally accepted. These include a defined territory, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations wiht other states. But even meeting these requirements isn’t a guarantee of recognition.
Ultimately, recognition hinges on political will. Each existing state – and international organizations like the United Nations – individually decides whether to acknowledge the legitimacy of another. This means a state can exist de facto (in reality) without being recognized de jure (legally).
The Role of Diplomacy
Bilateral diplomatic gestures are crucial in this process.Consider them carefully calibrated steps a country takes to signal its acceptance of a new entity. These actions aren’t just symbolic; they actively shape the international landscape.
Think of it as building relationships. A nation seeking recognition actively engages in dialog, establishes formal ties, and demonstrates its commitment to international norms. This proactive approach significantly increases its chances of gaining widespread acceptance.
A spectrum of Statehood
The territories aspiring to recognition exist on a broad spectrum. Hear’s a breakdown of the common categories:
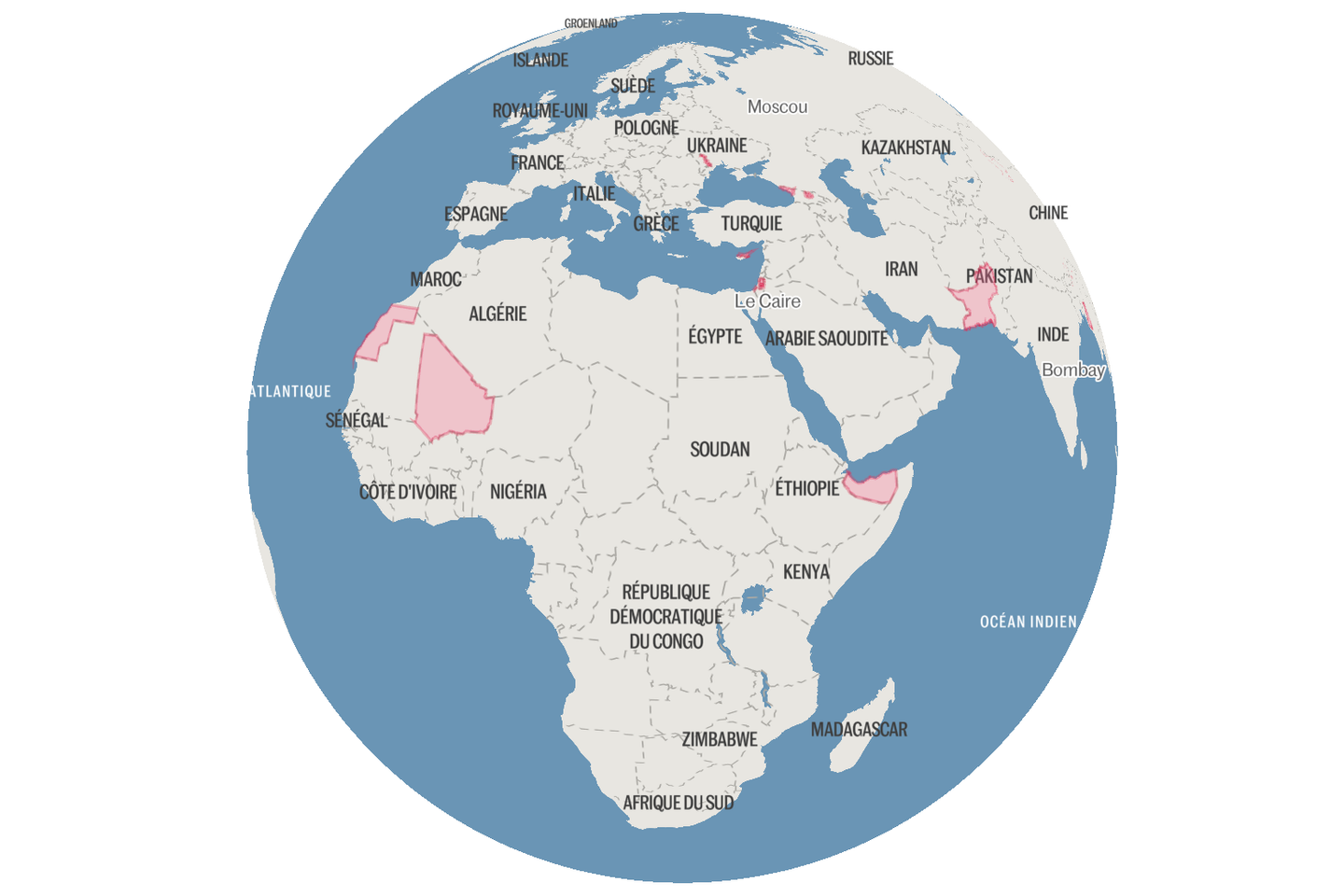
* Autonomous Territories: These regions possess some self-governance but lack fully developed state structures.Examples include areas like the Azawad and Baluchistan.
* States de Facto: These entities maintain relative stability and exercise control over a territory, but their sovereignty isn’t internationally acknowledged.Somaliland is a prime example.
* States de Facto and de jure: These are well-structured states with notable international engagement, yet face non-recognition from certain key players, like North Korea and its long-standing relationship with Paris.
Why Does Recognition Matter?
Recognition isn’t merely a formality. It unlocks a host of benefits for a newly formed state:
* International Legitimacy: Recognition validates the state’s existence on the world stage.
* Access to Resources: It opens doors to international aid, trade, and investment.
* Legal Standing: A recognized state can participate in international treaties and organizations.
* Protection Under International Law: Recognition provides a degree of protection against external interference.
The Path Forward
The journey to statehood is rarely straightforward. it requires a combination of internal stability, diplomatic skill, and favorable geopolitical conditions. You’ll find that navigating this complex landscape demands patience, persistence, and a deep understanding of international relations.
Ultimately, the decision to recognize a new state is a political one, reflecting a country’s own interests and values. It’s a process that continues to shape the world map and the relationships between nations.