The surprising Roles of Body Fat: Beyond Energy Storage
For years, body fat has been vilified as a health enemy. However, a closer look reveals a more nuanced picture. Fat isn’t simply a passive storage depot; itS a dynamic tissue with diverse functions, and even different types, each playing a unique role in our overall health. Understanding these distinctions – especially the roles of white, brown, and beige fat – is revolutionizing our understanding of metabolism, temperature regulation, and even cardiovascular health.
The Spectrum of Fat: White, Brown, and Beige
Traditionally, body fat was categorized into two main types: white and brown. More recently,a third type,beige fat,has entered the equation,adding another layer of complexity. These classifications aren’t just about color; they reflect fundamental differences in structure and function.
White Fat: The Energy Reservoir
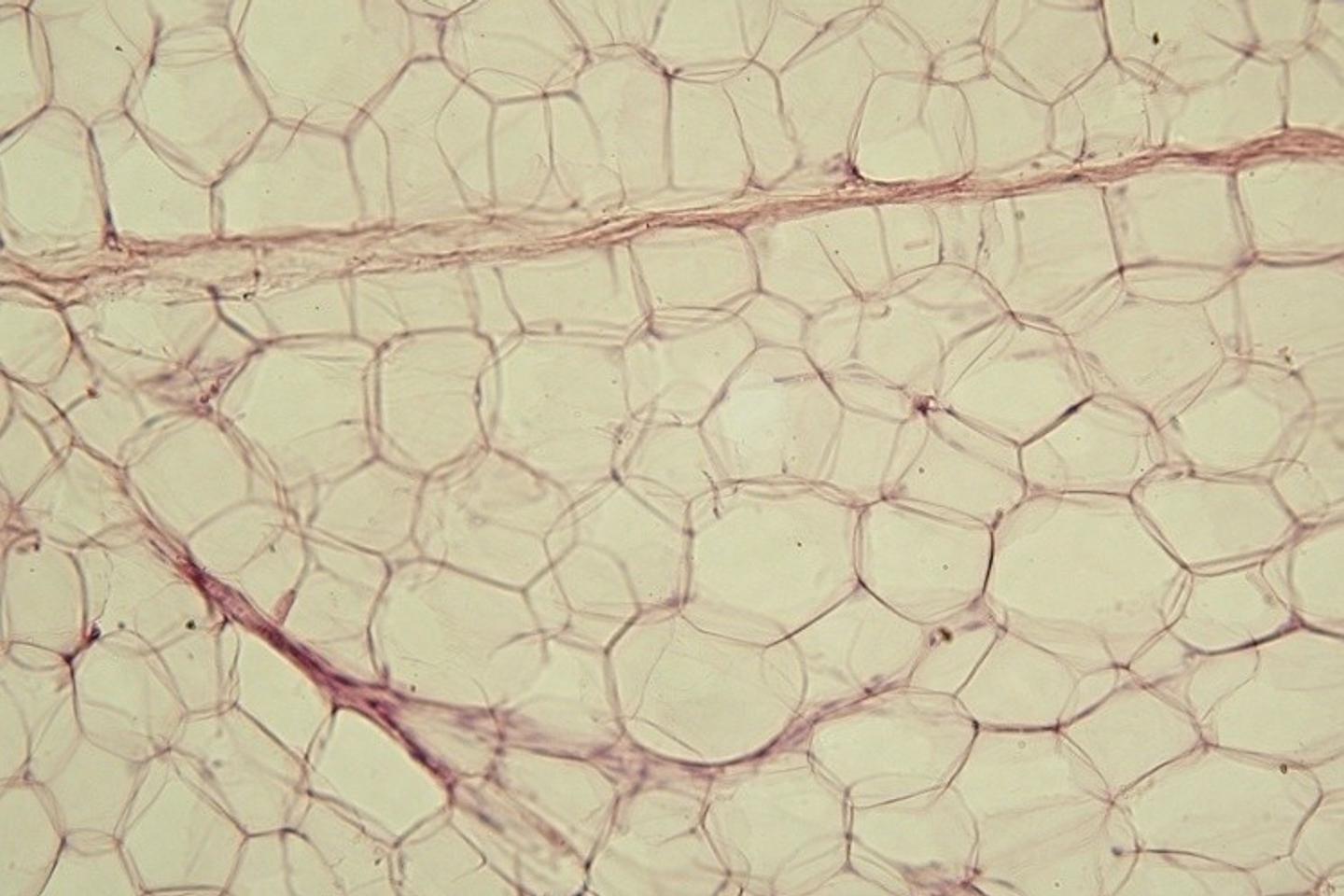
White adipose tissue (WAT) is the most abundant type of fat in the human body. Its primary function is to store energy in the form of triglycerides. This stored energy serves as a vital reserve during times of caloric deficit. While essential for survival, excessive accumulation of white fat is strongly linked to a range of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. Maintaining a healthy body fat percentage – generally considered between 14-31% for women and 6-24% for men, according to the American Council on Exercise – is crucial for overall well-being.
brown Fat: The Heat Generator
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) operates very differently. Instead of storing energy, BAT burns calories to generate heat. This process, known as thermogenesis, is particularly important for infants, who lack the ability to shiver effectively and rely on brown fat to maintain their body temperature. for a long time, it was believed that brown fat largely disappeared after infancy. However, research in 2009 revealed that adults retain small amounts of brown fat, primarily around the adrenal glands, collarbones, and spine. Interestingly, individuals with obesity tend to have less active, or even reduced amounts of, brown fat.
Beige Fat: A Hybrid with Potential
The revelation of beige fat, also known as “brite” (brown-in-white) fat, approximately fifteen years ago, added a fascinating twist to the story. Beige fat cells reside within white fat tissue and can be “activated” to behave more like brown fat, increasing energy expenditure and heat production. Recent research, published in Science on January 15th, has uncovered a surprising benefit of beige fat in mice: it plays a role in maintaining normal blood pressure by influencing the function of blood vessels.
The Future of Fat Research
The evolving understanding of adipose tissue is opening up exciting new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Researchers are actively exploring ways to stimulate the growth and activity of brown and beige fat as potential strategies for combating obesity, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular disease. Further examination into the mechanisms by which beige fat regulates blood pressure could lead to novel treatments for hypertension.
Ultimately, recognizing the complexity of body fat – and moving beyond the simplistic notion of “fat is bad” – is essential for promoting a more informed and effective approach to health and wellness.
Keywords: body fat, brown fat, white fat, beige fat, adipose tissue, metabolism, thermogenesis, weight management, obesity, cardiovascular health, blood pressure, metabolic disease.