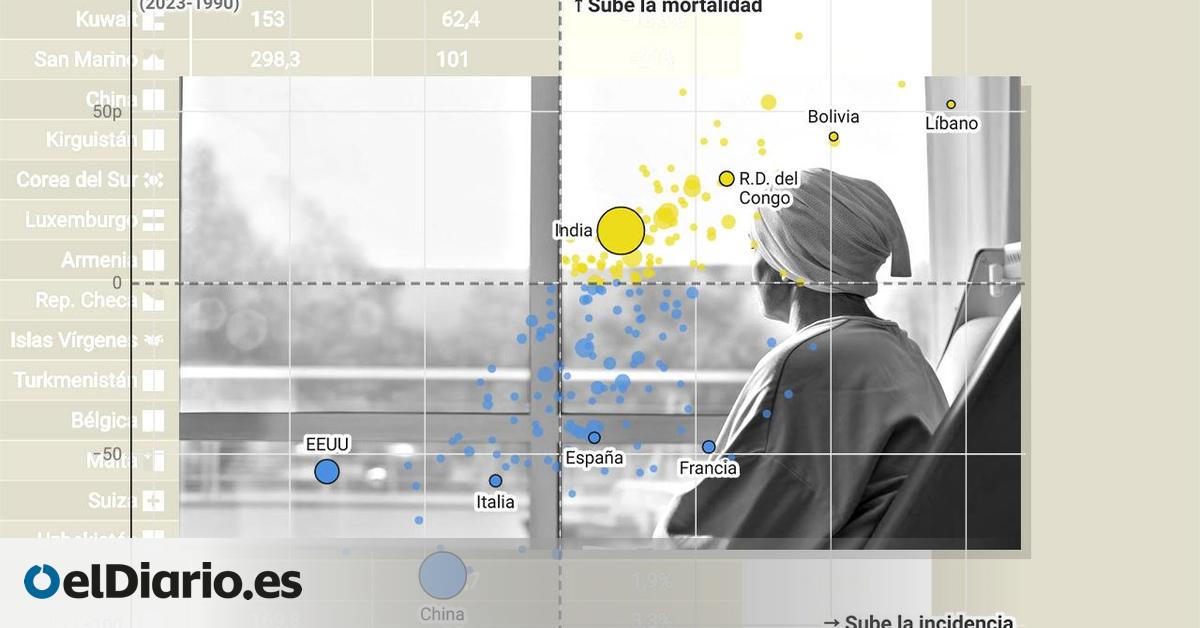
Gráficos de Yuly Jara.
Understanding data visualization is crucial in today’s information-rich world. It allows you to quickly grasp complex trends and insights that would otherwise be hidden in rows of numbers. Here’s what you need to know to effectively interpret and utilize visual data.
Why data Visualization Matters
Data visualization transforms raw data into easily digestible formats like charts, graphs, and maps. This process offers several key benefits: it identifies patterns, highlights outliers, and simplifies complex information. You can then communicate findings more effectively to others.
Common Types of Data Visualizations
Several visualization types cater to different data sets and analytical goals. here’s a breakdown of some popular options:
* Bar Charts: Ideal for comparing discrete categories. They clearly show differences in magnitude.
* Line Graphs: Best for displaying trends over time. You can easily see increases, decreases, and fluctuations.
* Pie Charts: Useful for illustrating proportions of a whole. However, they can become cluttered with too many slices.
* Scatter Plots: Reveal relationships between two variables. They help identify correlations and clusters.
* Histograms: Show the distribution of a single variable. You can understand the frequency of different values.
* Maps: Visualize geographical data. They highlight regional patterns and variations.
Key Principles for Effective Visualization
Creating impactful visualizations requires careful consideration. Here are some principles to guide you:
* Clarity: Prioritize clear labeling and concise titles. Avoid unnecessary clutter that distracts from the core message.
* Accuracy: Ensure your visualizations accurately represent the underlying data. Misleading visuals can erode trust.
* Simplicity: Choose the simplest visualization that effectively conveys your message. Avoid overly complex designs.
* Context: Provide sufficient context to help your audience understand the data. Include relevant annotations and explanations.
* color: Use color strategically to highlight key information. Avoid using too many colors, which can be overwhelming.
Tools for creating Visualizations
Numerous tools are available to help you create compelling visualizations. Some popular options include:
* Spreadsheet Software (excel, Google Sheets): Offers basic charting capabilities for simple data sets.
* Data Visualization Software (Tableau, Power BI): provides advanced features for creating interactive dashboards and reports.
* Programming Languages (Python,R): Enables highly customized visualizations with extensive libraries.
* Online Visualization Tools (Datawrapper, flourish): Offers user-pleasant interfaces for creating shareable visualizations.
Interpreting Visualizations Critically
It’s not enough to simply look at a visualization. You must interpret it critically to draw meaningful conclusions. Consider these points:
* Data Source: understand where the data came from and its potential biases.
* Scale and Axis: Pay attention to the scale of the axes.Manipulated scales can distort the perception of data.
* Correlation vs. Causation: Remember that correlation does not imply causation. just because two variables are related doesn’t mean one causes the othre.
* Outliers: Investigate any unusual data points. They may indicate errors or notable findings.
* overall Message: Identify the main takeaway from the visualization. What story is the data telling you?
I’ve found that taking the time to