Lab-Grown ‘Embryo-Like’ Structures Offer Revolutionary Path to Regenerative Blood Therapies
For decades, regenerative medicine has promised a future where damaged tissues and organs can be repaired – even grown – using a patient’s own cells. Now, a groundbreaking study from the University of Cambridge’s Gurdon Institute brings that future significantly closer. Scientists have successfully grown embryo-like structures in the lab capable of producing human blood cells, opening up unprecedented possibilities for treating blood disorders and revolutionizing bone marrow transplantation.
this isn’t about creating artificial embryos. It’s about meticulously recreating the vrey beginnings of human advancement – the crucial early stages of blood formation – without the need for eggs or sperm. This innovative approach utilizes the power of stem cells,offering a potentially limitless source of compatible blood for patients in need.
A Window into Early Human Development
The research, published in Cell Reports, represents a major leap forward in the rapidly evolving field of embryo modeling. Led by Dr. Jitesh Neupane and professor Azim Surani,the team harnessed the remarkable ability of human stem cells to self-organise. These aren’t just any stem cells; they can be derived from any cell in the body, meaning a patient’s own cells could be used to generate a personalized blood supply.
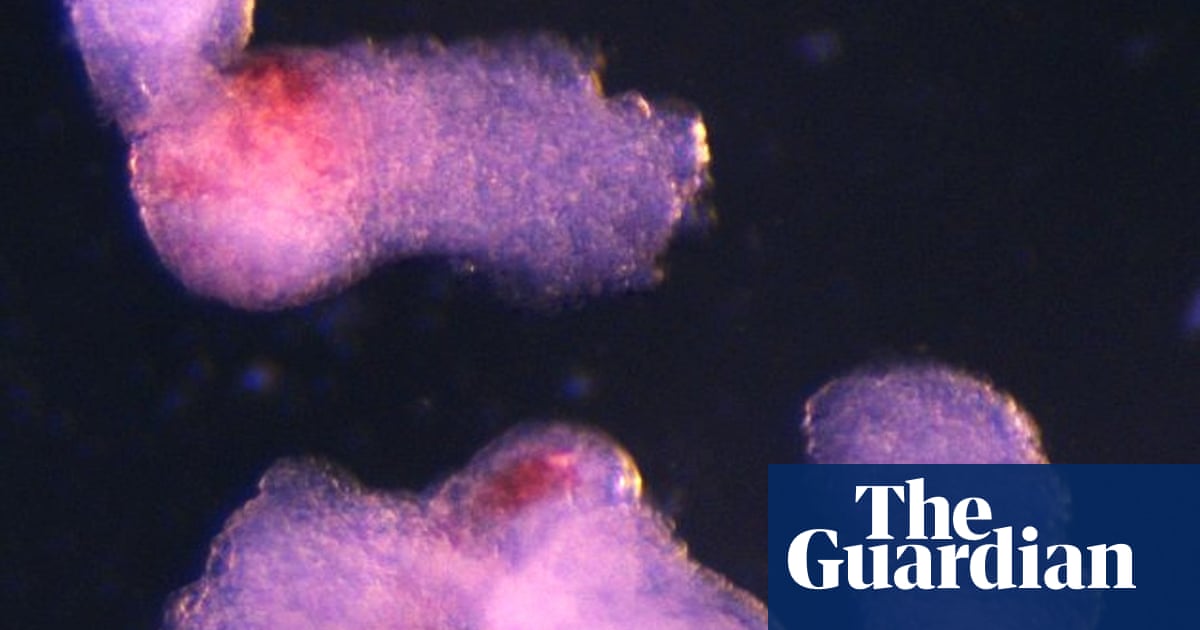
“It was an exciting moment when the blood-red colour appeared in the dish – it was visible even to the naked eye,” recalls Dr. Neupane. That vibrant colour signaled the successful formation of red blood cells, a critical component of human blood.
But the importance extends far beyond a visual confirmation. this model allows researchers to observe and understand the intricate processes that govern blood and immune system development in a way previously unachievable. “This sheds light on how blood cells naturally form during human embryogenesis,” explains dr. neupane, “offering potential medical advances to screen drugs, study early blood and immune development, and model blood disorders like leukaemia.”
Why This Approach is Different – and Better
Current methods for generating human blood stem cells in a lab often rely on complex cocktails of proteins. this new technique, however, elegantly mimics the natural developmental process. By allowing the stem cells to self-organize,the researchers have created a more physiologically relevant model,potentially leading to more effective and reliable therapies.
Professor surani emphasizes the long-term implications: ”Although it is still in the early stages, the ability to produce human blood cells in the lab marks a meaningful step towards future regenerative therapies – which use a patient’s own cells to repair and regenerate damaged tissues.”
Building the Foundations of Life – In a Dish
The team meticulously replicated conditions mirroring the third and fourth weeks of human pregnancy. Crucially, the model was designed to exclude the development of tissues that would form the placenta, yolk sac, or brain – eliminating any theoretical potential for the structure to develop into a full embryo. As Dr. Neupane clarifies, “This is a minimalistic system,” focused solely on the development of blood and early heart structures.
Under the microscope, the researchers observed a remarkable process of self-institution. Within two days, the stem cells arranged themselves into the three fundamental germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm - which form the blueprint for the entire human body. By day eight, the team witnessed the formation of beating heart cells. and by day 13,the telltale red patches of blood appeared,confirming the successful generation of blood stem cells.
These lab-grown blood stem cells weren’t just present; they were functional, demonstrating the ability to differentiate into various blood cell types, including oxygen-carrying red blood cells and vital immune system components like white blood cells.
The Future of Blood-Based Therapies
This research isn’t just a scientific curiosity; it’s a potential game-changer for patients suffering from blood disorders, those awaiting bone marrow transplants, and individuals requiring blood transfusions. The ability to generate fully compatible blood from a patient’s own cells eliminates the risk of rejection and drastically reduces the reliance on donor availability.
While further research is needed to refine the process and ensure safety and efficacy, this study represents a monumental step towards a future where regenerative medicine can truly deliver on its promise. The Gurdon Institute’s work offers a beacon of hope for millions, paving the way for personalized, life-saving therapies built on the very foundations of human development.