Beyond BMI: How Your Gut Microbiome & Metabolome Reveal True Metabolic Health
For decades, Body Mass Index (BMI) has been the go-to metric for assessing weight status and related health risks. Though, increasingly, it’s becoming clear that BMI alone paints an incomplete picture. It fails to capture the nuances of metabolic health, especially in individuals falling within the “normal” or “overweight” ranges. Emerging research reveals a far more complex interplay between your gut microbiome, your metabolome (the collection of small molecules created during metabolism), and your risk for metabolic dysfunction.
This isn’t just about weight; it’s about how your body processes energy and nutrients. Let’s dive into what this means for you and your health.
The Limitations of BMI
BMI,while easy to calculate,doesn’t differentiate between muscle mass and fat mass. Two individuals with the same BMI can have drastically different body compositions and metabolic profiles. This is where the concept of “metabolic obesity” comes into play – a state of metabolic dysfunction self-reliant of a high BMI. You can be at a “normal” weight and still be metabolically unhealthy.
Introducing metBMI: A More Precise assessment
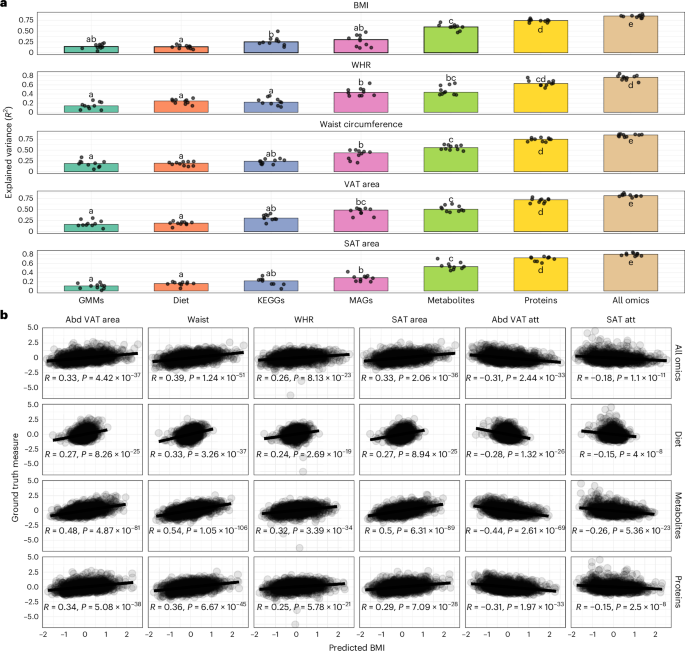
Researchers are now developing more sophisticated tools to assess metabolic risk. One promising advancement is “metBMI,” a metric that integrates data from multiple “omics” layers – including metabolomics, proteomics, and metagenomics (gut microbiome analysis).
Here’s how metBMI works and why it’s a game-changer:
* Beyond Weight: metBMI doesn’t just consider your weight. It analyzes hundreds of circulating metabolites - the byproducts of your body’s metabolic processes.
* Microbiome Connection: It incorporates data about the composition and function of your gut microbiome.This is crucial because your gut bacteria profoundly influence how you metabolize food and regulate energy balance.
* Superior Risk Stratification: Studies show metBMI is considerably better at predicting metabolic risk than BMI alone. It can identify individuals at risk before they reach obesity-defining thresholds.
* Predicting Treatment Response: Interestingly, metBMI can even predict how well you’ll respond to weight loss interventions, like bariatric surgery. Higher metBMI residuals (the difference between your predicted and actual metBMI) were associated with less weight loss after one year in a recent study.
The Gut-Metabolome Connection: A two-Way Street
The relationship between your gut microbiome and your metabolome isn’t a one-way street. It’s a dynamic, bidirectional interaction.
Here’s what the research reveals:
* Microbiome as a Proxy: Your gut microbiome doesn’t just reflect your metabolic state; it actively mediates it. Specific bacterial species and their metabolic products directly influence metabolic risk factors.
* Metabolite Mediation: Researchers have identified over 300 pathways linking the microbiome to your health, primarily through circulating metabolites.These metabolites act as messengers, carrying signals between your gut bacteria and your organs.
* Dysbiosis & Dysfunction: Disruptions in this gut-metabolome interplay - known as dysbiosis – can contribute to metabolic dysfunction, even in individuals with a normal BMI.
* Key players: Certain bacteria, like Ruminococcus gnavus and aerotolerant/oral bacteria, have been linked to unfavorable metabolic profiles. Shifts in microbial function, such as increased nitrate respiration and decreased methanogenesis, also play a role.
What Does This Mean for You?
Understanding the gut-metabolome connection empowers you to take a more proactive approach to your health. While metBMI isn’t yet widely available in clinical practice, the underlying principles are actionable:
* Focus on Diet: A diverse, plant-rich diet fuels a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.Prioritize fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods.
* Lifestyle Matters: Regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep all contribute to a balanced gut microbiome and optimal metabolic function.
* Personalized Approaches: As research advances, we’ll likely see more personalized interventions based on your unique microbiome and metabolome profiles.
* Don’t Rely Solely on BMI: Talk to your doctor about a comprehensive metabolic assessment that goes beyond BMI.
**The Future of