The $5 Trillion Potential of Advanced Robotic Hands: A Deep Dive
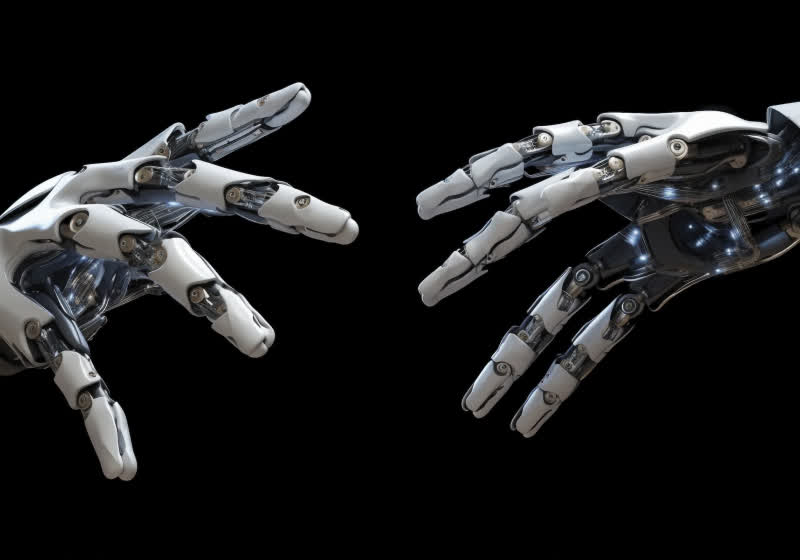
The quest to replicate the human hand in robotics represents a pivotal challenge – and a massive chance. As of October 26, 2025, engineers globally are intensely focused on developing robotic hands capable of the dexterity, sensitivity, and adaptability of their biological counterparts. While advancements in locomotion and balance have propelled humanoid robot development, the lack of truly capable hands remains a critical impediment to widespread industrial and commercial adoption. This isn’t merely an engineering problem; it’s a gateway to unlocking an estimated $5 trillion in economic value,according to recent analyses by the Robotics Industries Association (RIA). This article will explore the complexities of robotic hand design,current breakthroughs,real-world applications,and the future trajectory of this rapidly evolving field.
The Core Challenge: Mimicking Human Dexterity
The difficulty lies not just in replicating the structure of the hand, but also its function.Human hands aren’t simply mechanical grippers; they’re incredibly versatile tools capable of performing a vast range of tasks, from delicately handling fragile objects to applying precise force.This versatility stems from a combination of factors: intricate skeletal structure, complex musculature, and a refined sensory system. Current robotic hands often excel at specific tasks – like picking and placing – but struggle with adaptability and generalization.
A key issue is achieving a natural and adaptable grip. Unlike rigid robotic claws, human hands conform to the shape of objects, distributing force evenly and preventing slippage. This requires not only flexible joints but also advanced control algorithms that can interpret sensory feedback and adjust grip parameters in real-time. Recent research published in Science Robotics (November 2024) highlights the importance of ”soft robotics” – utilizing compliant materials and fluidic actuation to create hands that are more adaptable and less prone to damaging objects.
Current Breakthroughs in Robotic Hand Technology
Several promising avenues are being explored to overcome the limitations of existing robotic hands. These include:
* Underactuated Hands: These hands utilize fewer actuators (motors) than degrees of freedom,relying on clever mechanical design and passive compliance to achieve dexterity.This reduces complexity and cost, making them suitable for a wider range of applications. Think of it like a human hand naturally curling around an object – it doesn’t require individual muscle control for every finger joint.
* Soft Robotics & Fluidic Actuation: As mentioned previously, soft robotic hands, often constructed from silicone or other flexible materials, offer inherent compliance and adaptability. Fluidic actuation – using pressurized fluids to control movement - provides a smooth and precise form of control. Companies like Soft Robotics Inc. are leading the charge in this area, developing grippers for food handling and logistics.
* advanced Sensors & Haptic Feedback: Integrating high-resolution tactile sensors into robotic hands allows them to “feel” objects, providing crucial information about shape, texture, and force. Haptic feedback systems transmit this sensory information back to the operator (in teleoperation scenarios) or to the robot’s control system,enabling more precise and nuanced movements. Researchers at Stanford University have developed artificial skin sensors with sensitivity comparable to human fingertips.
* AI-Powered Control Algorithms: Machine learning algorithms, notably reinforcement learning, are being used to train robotic hands to perform complex tasks without explicit programming. These algorithms allow the hand to learn from its mistakes and adapt to new situations,improving its performance over time. Google’s work with its Shadow Dexterous Hand is a prime example of this approach.
| Feature | Conventional Robotic Hands | Advanced Robotic Hands (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Actuation | Multiple Motors, Rigid joints | Underactuation, fluidic Actuation |
| Materials | Metal, Hard Plastics | Silicone, Compliant Polymers |
| Sensors | Limited Force/Torque sensors | High-Resolution Tactile Sensors, Proprioception |
| Control | pre-programmed Movements | AI-Powered, Rein
|





![Bangladeshi Singer Attack: 25 Injured as Concert Disrupted in [Location – if known, add here] Bangladeshi Singer Attack: 25 Injured as Concert Disrupted in [Location – if known, add here]](https://i0.wp.com/publicnewsupdate.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/ibivg8ko_singer-james-concert_160x120_27_December_25.jpg?resize=150%2C100&ssl=1)
![Wearable Tech & Frailty: Early Detection for Seniors | [Year] Wearable Tech & Frailty: Early Detection for Seniors | [Year]](https://i0.wp.com/www.futurity.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/frailty-wearable-tech-elderly-care-1600.jpg?resize=150%2C100&ssl=1)


