Rigorous Statistical Design Underpins ARGO: A Deep Dive into teh Clinical Trial Methodology
The ARGO clinical trial, investigating the efficacy and safety of SLK (a novel therapeutic agent) in patients with active psoriatic arthritis, employed a meticulously designed statistical plan to ensure robust and reliable results.This document provides a detailed overview of the statistical methodologies utilized, highlighting the strategies implemented to control for error rates, manage missing data, and appropriately interpret the findings. Understanding these methods is crucial for evaluating the validity and clinical significance of the ARGO study outcomes.
Study Design & Populations:
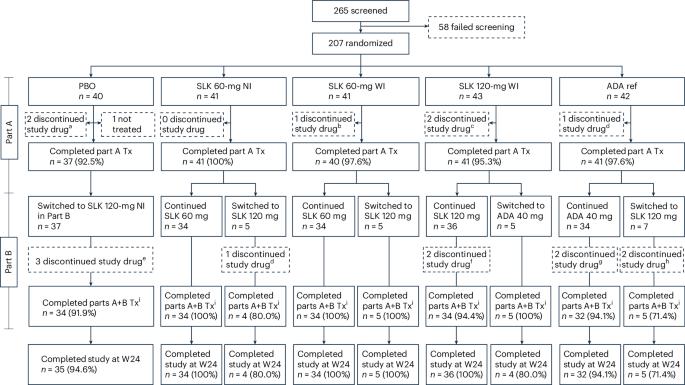
The ARGO trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Patients were randomized to one of four treatment arms: placebo (PBO), SLK 120mg weight-Matched Injection (WI), SLK 60mg WI, or SLK 60mg Needle-Injection (NI). An additional arm, treated with an approved anti-inflammatory drug (ADA), served as an active reference arm.Critically, the ADA arm was not powered for direct statistical comparison with SLK or placebo; its primary function was to provide a clinical benchmark for observed responses.
The primary analysis population was the Intent-to-Treat (ITT) population, encompassing all randomized patients. Safety analyses focused on patients who received at least one dose of the study treatment. This approach minimizes bias and ensures the results are representative of the broader patient population.
Statistical Analysis Plan: A Hierarchical, Controlled Approach
The statistical analysis plan was structured to address the inherent challenges of multiple comparisons and the inclusion of multiple dose arms. A fixed-sequence hierarchical testing procedure was implemented for the primary endpoint (ACR50 response at week 12) and key secondary endpoints (ACR20 response and PASI 90 response at week 12). This hierarchical approach is a cornerstone of rigorous clinical trial design, preventing inflated Type I error rates (false positives).
Here’s how the hierarchy functioned:
- Sequential Testing: Testing proceeded sequentially through the defined hierarchy. If a null hypothesis was not rejected at a given level, no further confirmatory testing was conducted for subsequent endpoints. This conservative approach prioritizes confidence in the initial findings.
- Bonferroni-Holm Correction: Given the multiple SLK dose arms, the Bonferroni-Holm procedure was applied to control for testing across induction arms for each endpoint. This involved a step-down adjustment of the significance level (α). The arm demonstrating the smallest p-value was initially tested against α = 0.025. If significant, the next arm with the largest p-value was tested against α = 0.05, and so on.
- Dose Arm Progression: Only after successfully navigating the hierarchical testing for SLK 120mg WI and SLK 60mg WI would the SLK 60mg NI arm be evaluated, using an α level of 0.05 for the primary endpoint and sequentially for key secondary endpoints.
This multi-layered approach to statistical control demonstrates a commitment to minimizing the risk of spurious findings and maximizing the reliability of the results.
Analytical Methods & modeling:
* Pairwise Comparisons: Logistic regression models were employed to assess pairwise comparisons between placebo and each SLK dose arm. These models incorporated fixed effects for treatment and pre-defined stratification factors (sex and prior biologic use) to account for potential confounding variables. Odds Ratios (ORs), risk differences, 95% Confidence Intervals (CIs), and two-sided p-values were calculated.
* Mixed-Effects Model for Repeated Measures (MMRM): Continuous endpoints were analyzed using an MMRM. This complex statistical technique effectively handles missing data and accounts for within-subject correlation,providing more accurate and reliable estimates of treatment effects. The model included treatment arm, visit, sex, prior biologic exposure, and a treatment-by-visit interaction as fixed effects.
* Logistic Regression for Dichotomous Endpoints: Dichotomous secondary endpoints were analyzed using logistic regression, providing insights into the association between treatment and response.
Handling Missing Data: A Robust NRI Approach
Missing data is a common challenge in clinical trials. ARGO employed a Non-Responder Imputation (NRI) method for dichotomous primary and key secondary endpoints. Under NRI, patients were considered non-responders if they discontinued the study before week 12, had missing data at baseline or week 12, or used prohibited medications.This conservative imputation strategy minimizes bias by assuming missing data represents treatment failure. For continuous endpoints, the MMRM inherently addresses missing data within its modeling framework.
**Part B