states Voice Critically important Concerns Regarding Medicaid Work Requirement implementation: A Looming Challenge to Access and Administrative Capacity
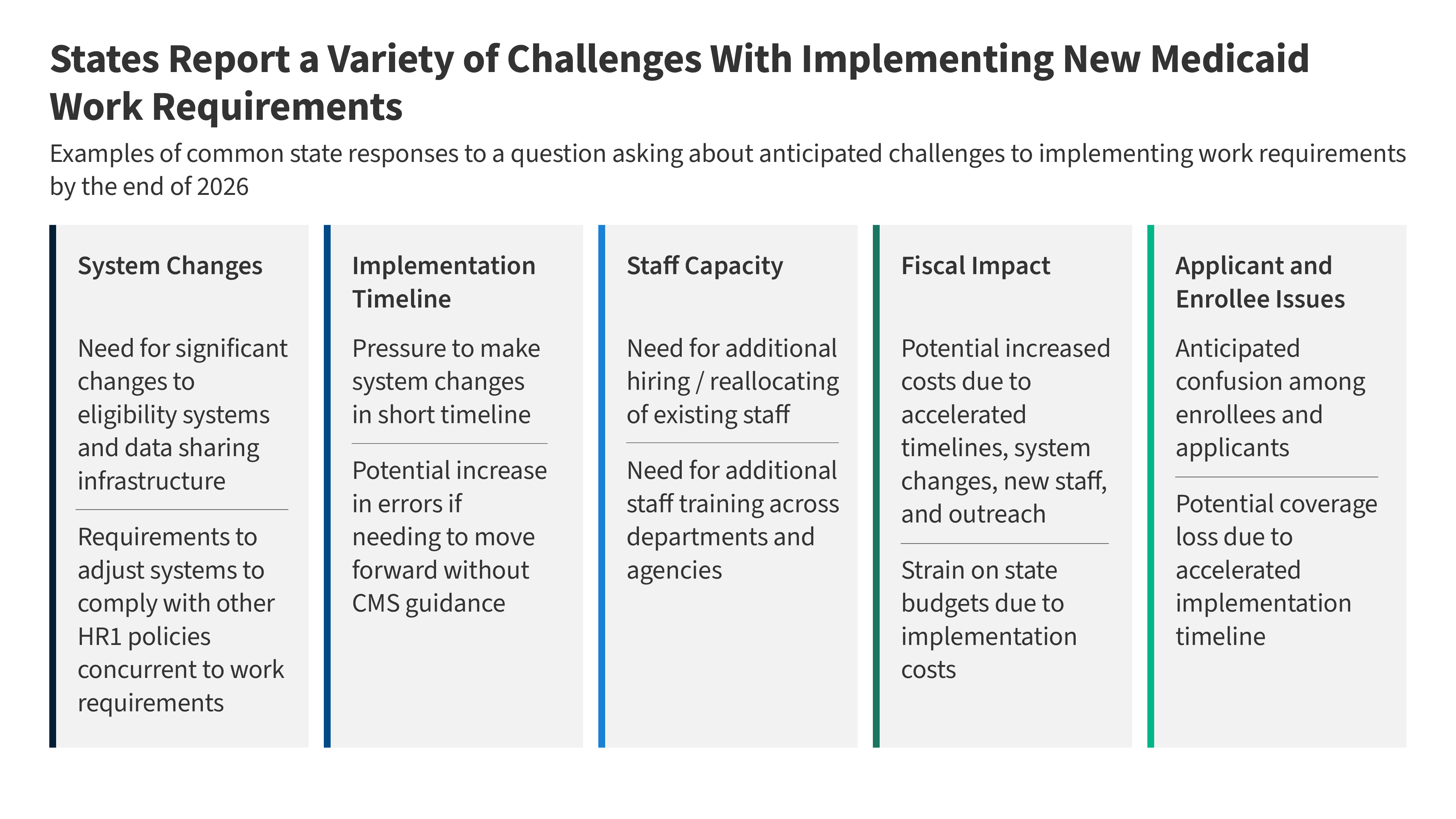
Recent feedback from state Medicaid agencies reveals substantial apprehension regarding the impending implementation of new work requirement policies, raising serious questions about their feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and potential impact on vulnerable populations. these concerns, gathered thru direct state reporting, highlight a critical need for clearer guidance from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and a realistic assessment of implementation timelines. This analysis synthesizes those concerns, offering a comprehensive overview of the challenges states face and the potential consequences for Medicaid beneficiaries.
alignment with Federal Expectations & implementation Timelines: A Recipe for Error
A consistent theme across state responses is the misalignment between the federal expectations for implementation and the practical realities on the ground. several states explicitly characterized the current deadlines as “unrealistic,” predicting that a rushed implementation will inevitably lead to increased error rates and, consequently, unnecessary coverage losses. This isn’t simply a matter of bureaucratic delay; it’s a fundamental concern about ensuring accurate eligibility determinations and protecting access to vital healthcare services. Specifically,states are urgently seeking clarity on key definitions – notably,”medical frailty” - and the permissible use of self-attestation,both of which directly impact system configurations and eligibility decisions. Without this guidance, states are forced to proceed with uncertainty, increasing the risk of costly rework and systemic errors. The possibility of pursuing “good faith waivers” to delay implementation was also raised,but states emphasized the need for clear criteria and a streamlined application process.
Workforce Strain: A Capacity Crisis in the Making
Beyond policy ambiguities, states are grappling with significant workforce challenges. The anticipated surge in administrative workload – stemming from increased verifications, appeals, and enrollee inquiries - necessitates either the hiring of new staff or the reallocation of existing personnel. Crucially, this isn’t a simple staffing issue; it requires comprehensive training across departments and agencies (including SNAP) to ensure eligibility workers are fully equipped to navigate the new rules, exemption criteria, and documentation requirements. Several states highlighted that their teams are already heavily engaged in major, multi-year modernization projects, creating a critical strain on limited resources and perhaps delaying eligibility determinations for those not subject to the work requirements. This “spillover effect” could undermine the overall efficiency of the Medicaid program.
Financial Implications: Increased Costs & Budgetary Pressures
Even with the provision of $200 million in federal funding for systems development and the potential for increased federal matching payments (up to 90% for certain IT system changes), states are deeply concerned about the escalating costs of implementation. Systems changes, interagency agreements, state rulemaking, and comprehensive enrollee outreach all contribute to a substantial financial burden. The accelerated timelines, in particular, are driving up costs associated with contracts and system modifications.furthermore, the potential for new financial penalties for error rates in both SNAP and Medicaid adds another layer of risk, potentially influencing states’ approaches to system changes and prioritizing accuracy over speed.states are rightly concerned that these increased costs will exacerbate existing budgetary constraints.
Enrollee Impact: Confusion, Coverage Loss, and Equity Concerns
While not directly solicited, states proactively raised concerns about the potential impact on enrollees. Anticipated confusion regarding the new requirements is a major worry, and states recognize the need for robust outreach efforts.However, they also caution that premature communication without clear federal guidance could increase confusion if state assumptions diverge from CMS’s final interpretations. the risk of coverage loss due to the accelerated timeline is a significant concern, and states are actively exploring strategies to mitigate this. Specific vulnerabilities were identified, including enrollees in rural areas with limited internet access and those with jobs characterized by fluctuating work hours – populations who may face disproportionate challenges in meeting the new requirements.
Moving Forward: A Call for Collaboration and Realistic Planning
The consistent message from states is clear: prosperous implementation of these work requirements hinges on proactive collaboration with CMS, a realistic assessment of timelines, and adequate resources. Specifically, the following steps are critical:
* Immediate and Comprehensive Guidance: CMS must prioritize the issuance of clear, detailed guidance on key definitions, exemption criteria, and the permissibility of self-attestation.
* Flexible Implementation Options: Consideration shoudl be given to allowing states to pursue good faith waivers, with transparent criteria and a streamlined application process.
* Adequate Funding & Technical Assistance: Continued federal investment in systems development and technical assistance is essential to support states in navigating these complex changes.
* Ongoing Monitoring & evaluation: A robust monitoring and evaluation framework is needed to track implementation progress, identify challenges, and assess the impact on enrollee access and health outcomes.
Failing to address these concerns risks undermining the integrity of the Medicaid program, jeopardizing access to care for vulnerable populations, and creating significant administrative burdens for states. A collaborative, pragmatic approach is essential to ensure that these policies are implemented effectively and responsibly.