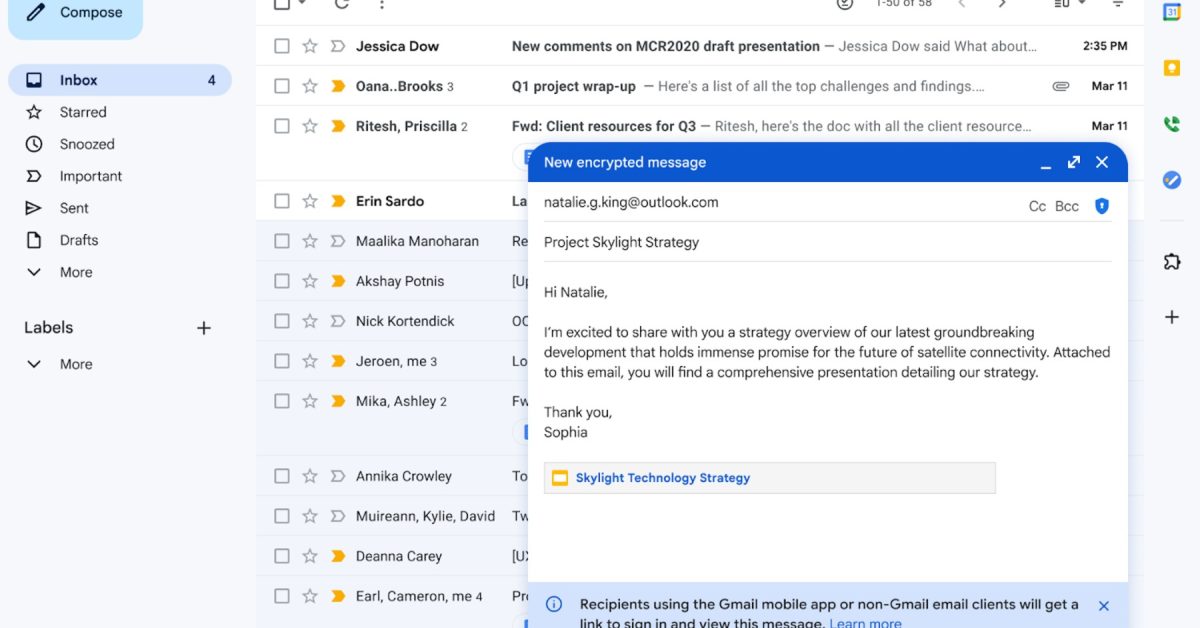
Gmail End-to-End Encryption: A Deep Dive into Client-Side Encryption & Enhanced Email Security (2025)
In a important move towards bolstering user privacy, Google is now rolling out end-to-end encryption (E2EE) within Gmail. This isn’t just for Gmail users anymore; the feature extends to recipients using othre email providers, marking a significant shift in how email security is approached. As of October 5, 2025, this rollout, initially announced on October 3rd, 2025, is poised to redefine email privacy standards, offering a layer of protection previously reserved for specialized, often complex, encryption methods. This article provides a extensive overview of Gmail’s client-side encryption (CSE), its implications, and how it compares to existing email security measures.
Understanding gmail Client-Side Encryption (CSE)
Traditionally, email encryption has largely relied on Transport Layer Security (TLS) during transit – protecting the email as it travels between servers. however, TLS doesn’t protect the email while its stored on email servers. Gmail’s CSE addresses this vulnerability by encrypting the email content on your device before it’s sent, and decrypting it on the recipient’s device. This means Google, or any third party intercepting the email on the server, cannot read the message content.
This is a crucial distinction. While Google already employs robust security measures, CSE adds a layer of privacy that puts the user firmly in control of their data. It’s a response to growing concerns about data breaches, government surveillance, and the increasing need for digital privacy. The implementation leverages S/MIME standards, a widely recognized protocol for secure email.
Did You Know? The initial rollout of Gmail’s CSE began in 2022, initially focused on Workspace customers.This broader release to all Gmail users represents a significant expansion of this security feature.
How Does Gmail CSE Work?
The process is designed to be remarkably user-friendly, despite the complex cryptography underpinning it. here’s a breakdown:
- encryption on Send: When you compose an email using CSE, gmail encrypts the message content using a key derived from your Google Account.
- Secure Transmission: The encrypted email is transmitted to Google’s servers and then to the recipient’s email server.
- Decryption on Receive: The recipient receives a notification and a link to a decryption portal. They must verify their identity (typically through a one-time password sent to their email address) to access the decryption key.
- Accessing the Message: Once authenticated, the recipient can decrypt and read the email within the Gmail interface.
It’s critically important to note that,as of now,the subject line and recipient list are not encrypted. This is a deliberate design choice to facilitate email filtering and association.However, Google has indicated they are exploring options for encrypting these elements in future iterations.
Who Benefits from Gmail CSE?
The benefits of Gmail’s CSE are wide-ranging:
- Journalists & Sources: Protecting sensitive communications with confidential sources.
- legal Professionals: Maintaining client confidentiality and adhering to legal privilege.
- Healthcare Providers: Ensuring HIPAA compliance and safeguarding patient data.
- Activists & Human Rights Workers: Communicating securely in environments with potential surveillance.
- Anyone Concerned About Privacy: Adding an extra layer of security to personal and professional correspondence.
Pro Tip: While CSE significantly enhances privacy, it’s not a silver bullet. Strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and vigilance against phishing attacks remain crucial components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Gmail CSE vs. Other Encryption Methods
Several email encryption methods exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses.