Priscilla K. Brastianos
2026-01-16 00:00:00
Study oversight
This Alliance study was designed by the principal investigators and conducted in accordance with the provision of the Declaration of Helsinki (2013) and Good Clinical Practice guidelines. The National Cancer Institute Central Institutional Review Board approved the protocol. All patients provided signed informed consent. The protocol document is included in the Supplementary Information.
Patients
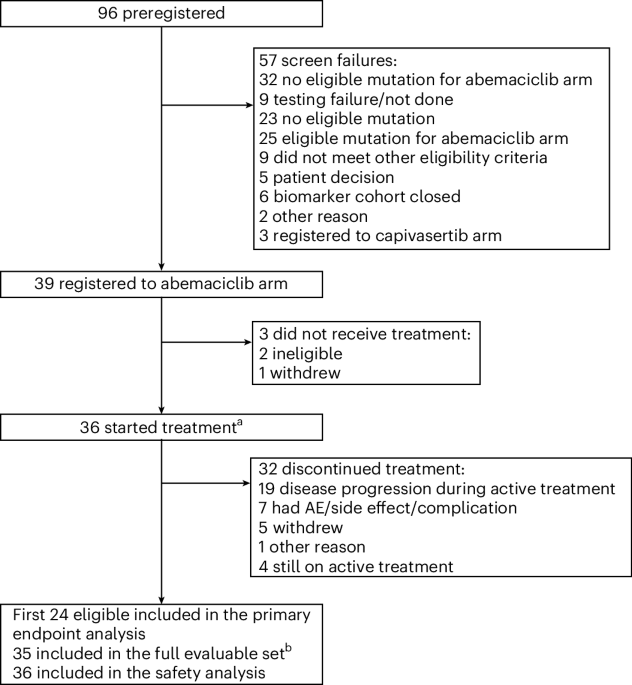
Eligible patients had intracranial grade 2 or 3 meningioma as documented by central pathology review, and measurable disease (as defined by bidimensionally measurable enhancing lesions with a minimum diameter of 10 mm). Central genetic testing was conducted on a tumor sample from each patient for study arm determination. Presence of an alteration in the CDK pathway or in NF2 in the tumor tissue was required for enrollment to the abemaciclib arm. Patients must have had progressive or residual disease as defined by residual measurable disease immediately after surgery, progressive measurable disease (increase in the size of the measurable lesion on imaging by 25% or more in 25 months) or progressive disease after radiation. Inclusion criteria also included steroid dosing stable for at least 4 days, no craniotomy for 28 days before or after registration, not pregnant and not nursing, ECOG performance status of 2 or less, no extracranial meningiomas, hemoglobin ≥8 g dl−1 recovered to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) grade 1 or less toxicity, except for residual alopecia, or grade 2 neuropathy and no chemotherapy, cancer-directed hormonal therapy or other investigational agents within 28 day of study treatment. Key exclusion criteria included active bacterial, fungal or detectable viral infection and a personal history of the following conditions: syncope of cardiovascular etiology, ventricular arrhythmia or pathological origin or sudden cardiac arrest.
Study design, treatment and endpoints
Central pathology review was conducted on the diagnostic hematoxylin and eosin slides to confirm the diagnosis of meningioma. In addition, integral molecular testing to evaluate the presence of an eligible gene mutation was performed on a single formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue block from the surgery that contained representative tumor tissue. For patients with specimens from multiple time points, it was recommended that the most recent specimen be submitted for genetic testing. For central genetic testing, there was a prespecified time limit of 21 days between central laboratory receipt of patient tumor specimen and notification of patient eligibility. Registration needed to occur within 28 days of receiving notification of patient eligibility from the central testing laboratory.
Abemaciclib was administered orally at 200 mg twice daily for 28-day cycles until disease progression, excessive toxicity, symptomatic neurological deterioration or study consent withdrawal. Guidelines for dose modifications were provided in the protocol. Patients underwent contrast-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging every 8 weeks using a consensus magnetic resonance imaging protocol40. Response was determined by local investigator review using standard Macdonald response criteria41. PFS6 was defined as the number of patients not having progressive disease or death within 6 months after the first day of treatment divided by the total number of evaluable patients. The RR was defined as the number of responses divided by the total number of evaluable patients. A patient was deemed to have a response if they had a confirmed partial or complete response.
Statistical design
Alliance A071401 is a prospective, multi-arm, phase 2 study evaluating the efficacy of targeted therapies in cohorts of patients with specific genetic mutations (Supplementary Information). Each mutation-based cohort/arm was designed to be evaluated separately using a phase 2 study design. A tumor sample from each patient underwent central pathology review and genetic testing for arm determination. Grading was based on the 2016 edition of the WHO classification of brain tumors42. Patients with recurrent or progressive grade 2 or 3 meningiomas harboring CDK pathway or NF2 mutations who met the eligibility criteria were enrolled in the abemaciclib arm; these results are reported in this article. The co-primary endpoints were PFS6 and RR after starting treatment. The trial was designed such that the treatment would be considered worthy of further study if either the PFS6 or RR endpoint was met. To accommodate the two co-primary endpoints, a Bonferroni correction43 was used to further constrain the one-sided type I error (bounded at 5% per endpoint). EAST v.6.3 and PASS 15.01 were used for the power calculations.
The first 24 patients who met the eligibility criteria, signed the consent form and began treatment were considered evaluable for the analysis of the primary endpoint decision rule. Twenty-four evaluable patients provided at least 85% power to detect a true PFS6 rate of at least 41.5%, with a significance level of 0.02 against the null hypothesis of 15% PFS6 rate. If at least eight patients (at least 31.1%) demonstrated PFS6 among the 24 evaluable patients, the agent would be considered worthy of further testing in this mutation-defined grade 2 or 3 cohort. The PFS6 hypothesis was derived from historical benchmark data from a comprehensive review of prior trials of medical therapies in patients with meningiomas, where PFS6 for grade 2 or 3 meningiomas ranged from 0 to 29% (ref. 1). Twenty-four evaluable patients provided at least 89% power to detect a true RR of at least 20%, with a significance level of 0.021 against the null hypothesis of 2.5% RR. If at least three responses (at least 12.5%) were observed among the 24 evaluable patients, the agent would be considered worthy of further testing in this mutation-defined treatment arm. Overaccrual was allowed to account for potential non-evaluable patients and to more fully assess secondary endpoints of interest. Secondary endpoints included overall survival and PFS, which were summarized with Kaplan–Meier curves and estimates44. AEs, graded according to CTCAE v.4.0, were summarized as the number, frequency and severity of each event, the number and frequency of patients who experienced any AE, any AEs graded 3 or greater, and any AEs graded 4 or greater.
Data collection and statistical analyses were conducted by the Alliance Statistics and Data Management Center. Medidata Rave Electronic Data Capture was used to collect the clinical trial data. SAS v.9.4 was used for the data analysis. Data quality was ensured by review of the data by the Alliance Statistics and Data Management Center and by the study chairperson according to Alliance policies. All analyses were based on the study database frozen on 6 November 2024. Of note, this is a small phase 2 study; as such, we were not powered to do any specific subset analyses based on sex.
This study is monitored by the study team on a monthly basis. Reports containing a summary of accrual and AEs according to treatment arm are reviewed.
Targeted molecular profiling
Molecular profiling was conducted using anchored multiplex PCR technology for single-nucleotide variant, insertion or deletion (indel), and copy number detection in genomic DNA using the ArcherDx platform and Illumina NextSeq next-generation sequencing, as described previously16,45,46,47,48,49. Briefly, after histopathological review of tumor enrichment, genomic DNA was isolated from a FFPE tumor specimen, enzymatically sheared, end-repaired, adenylated and ligated with a half-functional adapter. Two hemi-nested reactions were used to generate a sequencing library targeting hotspots and full exons. Illumina NextSeq 2 × 150 bp paired-end sequencing data were aligned to the hg19 human genome reference. MuTect1 (ref. 46), LoFreq50, GATK47,48,49 and a laboratory-developed hotspot caller, were applied for single-nucleotide variant and indel variant detection. If one of the callers was positive, the variant call was flagged as positive. All such variants were manually reviewed by a molecular pathologist to ensure their accuracy. A copy number caller using a coverage distribution from a panel of normals was used to detect copy gain and loss. Variants were reported with Human Genome Variation Society protein and DNA nomenclature, followed by the referenced Ensembl transcript ID.
FISH
1p loss was assessed using FISH with FFPE tumor specimens. Briefly, 5-μm sections of FFPE tumor material were prepared, and an hematoxylin and eosin section reviewed, to select regions for hybridization that contained a majority of tumor cells. A dual-color FISH assay was performed using the Vysis LSI 1p36/LSI 1q25 Dual Color Probe (Abbott Molecular). Signal quantitation in 50 tumor cells was used to generate a 1p-to-1q ratio, with a ratio of less than 0.75 diagnosed as loss, and 0.75 or greater as maintenance.
IHC
IHC for protein biomarkers was performed using 5-μm FFPE sections on a Leica Bond III automated stainer (Leica Biosystems). Stains were scored by a board-certified pathologist (A.J.I.). The following antibodies were used: CDK4 clone DCS-35 (1:300 dilution, cat. no. sc-23896, Santa Cruz Biotechnology); cyclin D1 clone EP12 (prediluted, cat. no. PA0046, Leica Biosystems); Ki-67 clone MM1 (prediluted, cat. no. PA0118, Leica Biosystems); p16 clone E6H4 (1:4 dilution, cat. no. 725-4793, Roche Diagnostics).
Statistical analysis of exploratory biomarkers
Patients were included in this analysis if they were eligible and had at least one posttreatment disease response assessment. Those with best response of stable diseases, partial response or complete response were classified as having CB, and those with best response of progressive disease were classified as no CB. Summary statistics were generated; Wilcoxon rank-sum and Fischer’s exact test P values were computed to test for differences in the distribution of continuous and categorical biomarkers across CB versus no CB groups. The association between biomarkers and CB was quantified using univariable logistic regression. The biomarkers were modeled as follows: Ki-67 as continuous; cyclin D1 as categorical (2 versus 3); p16 as continuous (0–3) and categorical (0, 1 versus 2, 3); CDK4 as continuous (0–3) and categorical (0, 1 versus 2, 3); 1p-to-1q FISH ratio as continuous (log2-transformed); 1p FISH mutation status as categorical (maintenance versus loss); and CDKN2A as categorical (normal versus mutation/deletion).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.