Breaking Through Barriers: Novel Approach overcomes Vaccine Resistance in Cancer Treatment
Recent advancements in cancer immunotherapy have shown remarkable promise, but overcoming resistance to these therapies remains a significant challenge.A groundbreaking study has demonstrated a strategy to revitalize immune function and achieve durable responses in patients previously unresponsive to vaccine therapy. This article delves into the details of this innovative approach, its implications for your cancer treatment options, and the future of personalized immunotherapy.
Understanding the Challenge of Vaccine Resistance
Cancer vaccines aim to train your immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. However, tumors often develop mechanisms to evade immune detection, leading to treatment resistance. These mechanisms frequently involve the exhaustion of T cells – the immune system’s primary cancer fighters. Essentially, T cells become “worn out” and unable to effectively eliminate tumor cells.
A Novel Strategy: Targeting T Cell Exhaustion
Researchers focused on reversing T cell exhaustion to enhance the effectiveness of cancer vaccines. Their approach involved a combination therapy designed to reinvigorate the immune response. the study focused on patients with advanced cancers who had previously shown no benefit from standard vaccine treatments.
Key Findings from the Clinical Study
The study yielded compelling results, demonstrating the potential of this new strategy. Here’s a breakdown of the key observations:
* Antigen Retention: Analysis of tumor samples confirmed that the targeted antigen remained present within the tumor even after treatment.This indicates the therapy wasn’t simply eliminating the target, but rather enabling the immune system to find it.
* HLA Expression: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) revealed consistent expression of HLA-I and HLA-II molecules – crucial for antigen presentation to T cells – both before and after treatment. This suggests the therapy didn’t disrupt the tumor’s ability to display cancer-specific markers.
* Antigen Presentation Machinery: Detailed RNA sequencing analysis showed no significant changes in the genes responsible for antigen presentation. This further supports the idea that the therapy works by boosting the immune response rather than altering the tumor itself.
* Immune Cell Shifts: imaging mass cytometry revealed significant changes in the tumor microenvironment. Specifically, researchers observed:
* an increase in granulocytes (a type of immune cell) within resistant tumors.
* A loss of B cells (another type of immune cell) in resistant tumors.
* Exhaustion Marker Reduction: IHC analysis demonstrated a notable decrease in immune exhaustion markers – like TIM3 and LAG3 – in responding tumors compared to resistant ones. This is a critical finding, as it directly links reduced exhaustion with positive treatment outcomes. Statistical analysis confirmed these differences were significant.
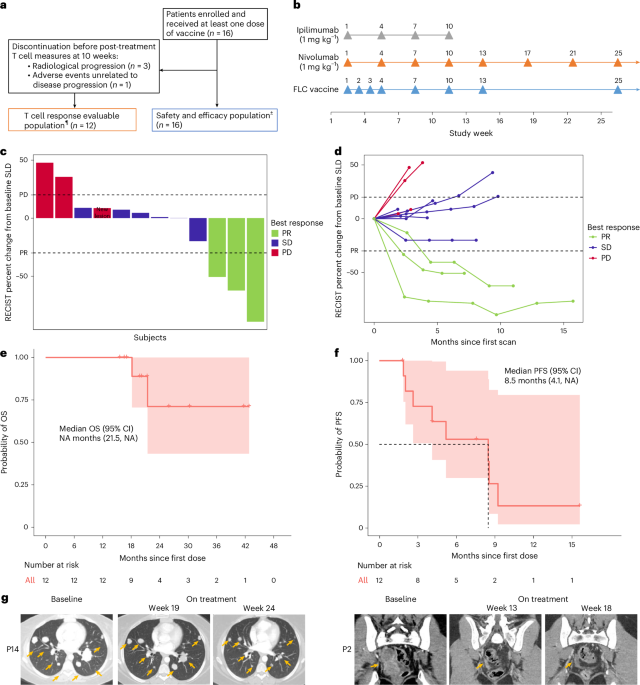
* Remarkable Patient Responses: Importantly, three out of three responding patients are currently without evidence of active cancer. Two patients underwent triumphant surgical removal of remaining disease, and remain cancer-free. The third patient’s remaining lesion is showing signs of tumor scar formation,indicating a positive response.
Case Study: P14 Demonstrates Re-Sensitization
One especially compelling case involved a patient (P14) who initially responded to treatment but later experienced disease progression. Remarkably, a subsequent rechallenge with ipilimumab – an immunotherapy drug - resulted in a renewed response, as evidenced by both radiologic scans and CyTOF analysis. This demonstrates the potential to re-sensitize tumors to immunotherapy after overcoming initial resistance.
What This Means for You
These findings offer a beacon of hope for individuals facing cancer treatment challenges. If you’ve previously been unresponsive to vaccine therapy,this research suggests that targeting T cell exhaustion could unlock a new path to remission.
* Personalized Immunotherapy: This approach highlights the importance of personalized medicine.understanding the specific mechanisms of resistance in your tumor is crucial for tailoring the most effective treatment strategy.
* Combination Therapies: Combining therapies that address both tumor-specific factors and immune function is likely to be key to achieving durable responses.
* Ongoing Research: The field of cancer immunotherapy is rapidly evolving. Continued research is essential to refine these strategies and expand their applicability to a wider range of cancers.
The Future of Cancer Immunotherapy
This study represents a significant step forward in our fight against cancer.By focusing on restoring immune function, researchers are opening up new avenues for treatment and offering renewed hope